Giant Cell Arteritis
What is giant cell arteritis?
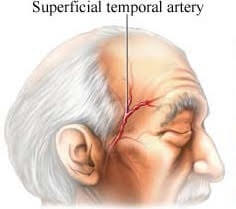
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is an urgent, inflammatory condition of medium sized blood vessels in the body. It most commonly affects blood vessels in your brain. It can affect the blood vessels around the temples, which is how it is also known as “temporal arteritis”. When the arteries become inflamed, they swell and can block the blood flow to certain parts of the body, especially the eyes.
What happens in giant cell arteritis?
When the blood flow to the eye is blocked, it can cause sudden, painless, total loss of vision. It generally first involves one eye, but if the disease goes untreated, it can affect the second eye causing permanent total vision loss in both eyes within a two-week time window. Vision loss is permanent.
Who is at risk for giant cell arteritis?
Giant cell arteritis occurs in adults, rarely under the age of 50. Generally, it occurs between the ages of 70 and 80. Women are twice as likely to have GCA, and it is more common in people with Northern European descent. A condition called polymyalgia rheumatica also puts patients at increased risk for GCA.
What are the symptoms of giant cell arteritis?
Sudden, painless vision loss of one eye is the main symptom of GCA, however it is generally accompanied by one or more other symptoms. These symptoms include:
- Headache
- Scalp tenderness
- Jaw pain/tiredness (especially when chewing)
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Flu-like symptoms
- Double vision
- Blurred vision







